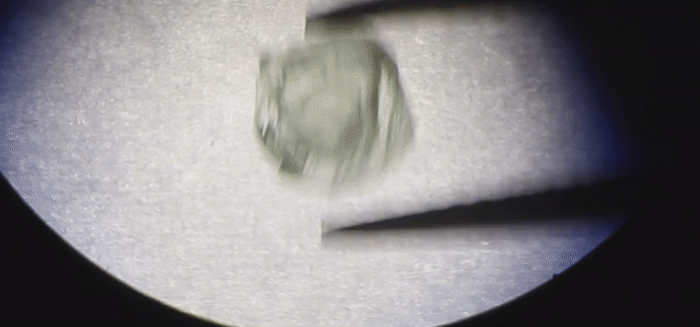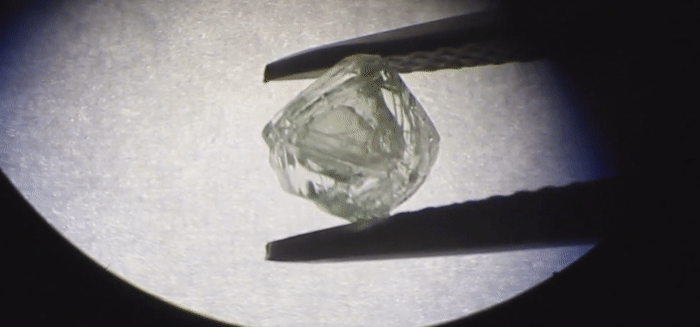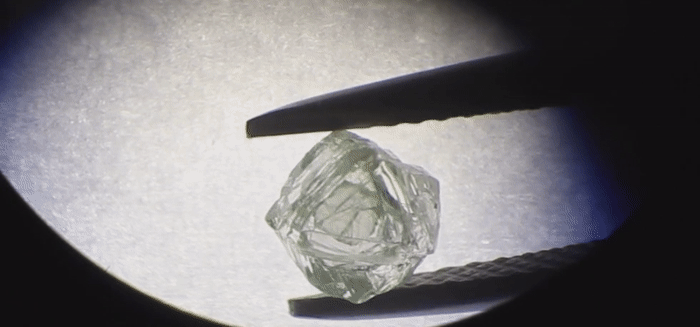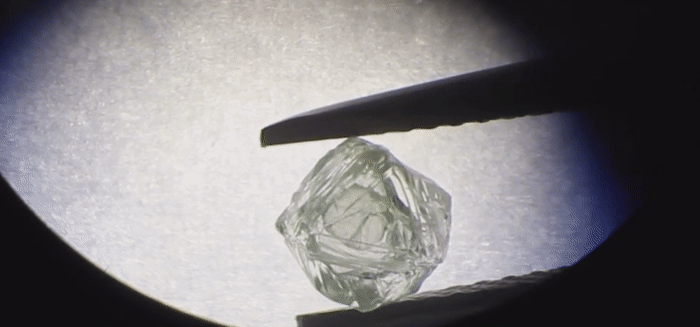
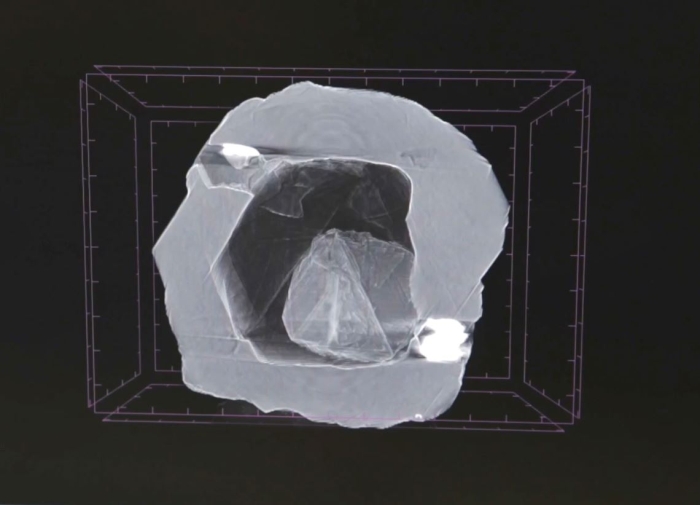
Humans have been mining diamonds for a long time, but a new stone hauled from the belly of the Earth could very well be a first. The diamond itself is hollow – and inside is another diamond, freely moving around.
It was discovered in a Russian mine in Siberia, and has been named the Matryoshka Diamond, after the Russian nesting
matryoshka dolls.
But a diamond in a diamond? That, according to Russian diamond mining group ALROSA, is a new one.
The Matryoshka Diamond is not a huge stone – just 0.62 carats (0.124 grams), with maximum dimensions of 4.8 x 4.9 x 2.8 millimetres. The inner diamond is even tinier – 0.02 carats (0.004 grams), measuring just 1.9 x 2.1 x 0.6 millimetres.
Sharp eyes detected something unusual about the stone during the sorting process, and it was sent to ALROSA’s Research and Development Geological Enterprise for assessment. There, scientists subjected the diamond to Raman and infrared spectroscopies, and X-ray microtomography.
(Alrosa PJSC)
„The most interesting thing for us was to find out how the air space between the inner and outer diamonds was formed,”
said Oleg Kovalchuk of ALROSA’s Research and Development Geological Enterprise. The researchers have a couple ideas which involve processes that may have occurred in Earth’s mantle.
According to one of their hypotheses, „a layer of porous polycrystalline diamond substance was formed inside the diamond because of ultra-fast growth, and more aggressive mantle processes subsequently dissolved it. Due to the presence of the dissolved layer, one diamond began to move freely inside another, just like a matryoshka nesting doll.”
X-ray of the Matryoshka Diamond. (Alrosa PJSC)
They also estimate that the diamond may be over 800 million years old, although that is yet to be verified. According to a Bloomberg report, the diamond is going to be sent to the Gemological Institute of America for further analysis.
Because it’s such a rare find, the company has yet to estimate its worth.
„As far as we know, there has been no such diamond in the history of global diamond mining,”
Kovalchuk said.
„This is really a unique creation of nature, especially since nature abhors a vacuum. Usually, in a case like this, the minerals would be replaced by others without forming a cavity.”

Oamenii au excavat după diamante de mult timp, dar o nouă piatră smulsă din burta Pământului ar putea foarte bine să fie prima de acest fel care a fost descoperită. Diamantul în sine este gol – iar în interior este un alt diamant, care se mișcă liber. A fost descoperită într-o mină rusă din Siberia și a fost numită Diamantul Matryoshka, după păpușile materne rusești matryoshka.
Includerile și defectele diamantelor sunt extrem de frecvente; de fapt, majoritatea diamantelor au câte un tip de defect, sau o bucată de mineral prinsă în interior. Nu este un lucru rău. Astfel de defecte conduc, frecvent, la creșterea valorii diamantului..
Dar un diamant într-un diamant? Asta, potrivit grupului rusesc de minerit de diamante ALROSA, este ceva complet nou.
Diamantul Matryoshka nu este o piatră uriașă – doar 0,62 carate (0,124 grame), cu dimensiuni maxime de 4,8 x 4,9 x 2,8 milimetri. Diamantul interior este și mai mic – 0,02 carate (0,004 grame), măsurând doar 1,9 x 2,1 x 0,6 milimetri.
O privire ageră a detectat ceva neobișnuit cu privire la piatră în timpul procesului de sortare și diamantul a fost trimis la întreprinderea geologică de cercetare și dezvoltare a ALROSA pentru evaluare. Acolo, oamenii de știință au supus diamantul la spectroscopii Raman și infraroșu precum și o microtomografie cu raze X.
„Cel mai interesant lucru pentru noi a fost să aflăm cum s-a format spațiul liber dintre diamantul interior și cel exterior”, a spus Oleg Kovalchuk, de la întreprinderea geologică de cercetare și dezvoltare a ALROSA. Cercetătorii au câteva idei care implică procese care au avut loc în mantia Pământului.Conform uneia dintre ipotezele lor, „în interiorul diamantului s-a format un strat de substanță poroasă policristalină, din cauza creșterii ultra-rapide, iar procesele mai agresive din manta au dizolvat-o ulterior. Datorită prezenței stratului dizolvat, un diamant a început să se miște liber în interiorul altuia, la fel ca o păpușă matryoshka „.
De asemenea, ei estimează că diamantul poate avea peste 800 de milioane de ani, deși acest lucru urmează a fi verificat. Potrivit unui raport Bloomberg, diamantul va fi trimis la Institutul Gemologic din America pentru analize suplimentare.
Deoarece este o descoperire atât de rară, compania nu trebuie să-i estimeze valoarea.
„Din câte știm, nu a existat un astfel de diamant în istoria minieră a diamantelor”, a spus Kovalchuk.
„Aceasta este într-adevăr o creație unică a naturii, mai ales că natura a generat un vid. De obicei, într-un caz ca acesta, mineralele ar fi înlocuite de altele fără a forma o cavitate.”
***
Publicat de Mihail
Fiind geamăn cu ascendant în săgetător sunt un extrovertit spre coleric de o curiozitate excesivă, perfecționist păgubos, împrăștiat, superficial, agnostic... și nimic din ce-i omenesc nu mi-e străin.
Being a Twin with ascendant in Sagittarius I am an extrovert up the choleric, of an excessive curiosity, a to the bitter end perfectionist, scattered, superficial, agnostic... and nothing that is human is foreign to me.
Vezi toate articolele lui Mihail